Welcome to the future of user experience design, where every swipe, tap, and click is finely crafted to make your digital journey seamless and efficient. In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, the Law of Fitts stands tall as a guiding principle for UX designers, revolutionizing how we interact with interfaces.
As we dive headfirst into 2024, it’s time to uncover the untapped potential of the Law of Fitts and witness how it paves the way for intuitive navigation, ensuring you effortlessly conquer the digital realm.
In this blog, we will explore the depths of Fitts law, its applications, impact on user efficiency, and potential to shape the digital experiences we encounter regularly. So buckle up and prepare to discover the secrets of Fitt’s Law as we discover its revolutionary power in the ever-changing realm of UI/UX design.
What Does the Law of Fitts Say?
The law of Fitts states that the time required to reach a target on a graphical user interface is determined by the size and distance of the target. Larger objects near the starting point require less time and effort to reach, leading to faster and more accurate interactions. This seemingly simple principle has far-reaching ramifications for UX design, influencing everything from button location to touch target size.
Picture this: you’re scrolling through your favorite software, effortlessly gliding around the interface, effortlessly landing on buttons, icons, and menu options. That smooth experience you’re having isn’t by chance. Fitt’s Law is in action here, a principle that blends psychology, ergonomics, and sheer UX magic to optimize how humans interact with digital interfaces. ate
Fitt’s Law has quietly been influencing the digital world around you, boosting your efficiency and elevating your user experience, whether swiping across a touchscreen or clicking through a web page.
Relation Between Fitts Law and User Interface Design
Fitts’ law instructs designers on optimizing interactive features such as buttons and icons by making them larger and positioning them closer to the user’s starting point, resulting in faster and more effective navigation. Fitts’ Law can also be used in menu design by frequently making accessible items larger and more readily placed.
Fitts’ Law aids in determining the right size of touch targets in mobile UI design, boosting usability on touchscreen devices. Fitts’ Law also optimizes drag-and-drop interactions, form design, and overall user experience, resulting in intuitive and simple-to-use interfaces. Designers may create aesthetically appealing and efficient interfaces that increase user pleasure and engagement by exploiting Fitts’ Law.

Importance of Fitts Law in UX Design
In the ever-evolving world of UX design, where every pixel counts, Fitts’ Law emerges as a true game-changer. This powerful principle is key to crafting user interfaces (UIs) that captivate and engage users in a seamless digital journey. So, what makes Fitts’ Law so vital? Let’s delve into its significance and discover how it revolutionizes UX design.
Easy Navigation
Fitts’ Law, at its core, serves as a compass, helping designers to create interfaces that users can easily navigate. Designers can strategically optimize UI design elements by recognizing that the time it takes to reach a target is determined by size and distance.
Consider a world where buttons and icons are ideally proportioned, easily accessible, and flawlessly responsive to user interactions. Fitts’ Law helps to realize this vision by ensuring that frequently used or vital parts take center stage, decreasing the time and effort required for users to complete their jobs. It’s the secret component that turns ordinary exchanges into pleasant ones.
Mobile Optimization
Fitts’ Law becomes even more important in the mobile era, spurring the optimization of touch targets for seamless interaction on touchscreen devices. Users can easily navigate interfaces with a few taps and swipes, thanks to designers that follow Fitts’ Law. Designers build a harmonious marriage between user intent and system reaction by considering touch targets’ appropriate size and spacing.
The end result? A world in which apps and websites respond to our touch in real-time, turning every encounter into a delightful dance. In short, Fitts law can aid in creating a mobile-friendly design for a website or app.
Applications of Fitt’s Law to UI/UX
- Button and Icon Placement
- Menu Design
- Touchscreen and Mobile Design
- Scrolling and Pagination
- Drag-and-Drop Functionality
- Link Placement
- Form Design
1- Button and Icon Placement
Fitt’s Law suggests that larger targets are easier to hit, so UX designers can use it to determine the optimal size and placement of buttons, icons, and interactive elements. Frequently used or critical elements should be larger and placed closer to the cursor’s starting position to reduce the time and effort required to reach them.

2- Menu Design
The law of Fitts can be applied to menu design by considering the size and positioning of menu items. Frequently accessed or important menu items should be larger and positioned closer to the cursor’s starting location to enhance usability and speed of selection.
3- Touchscreen and Mobile Design
With the rise of touchscreen devices, Fitt’s Law has become relevant in designing user interfaces for mobile applications. It helps determine the appropriate size and spacing of touch targets, ensuring they are large enough to be easily tapped with a finger, minimizing accidental touches, and improving overall user experience.

4- Scrolling and Pagination
Fitt’s Law can guide designers in deciding the size and placement of scroll bars or pagination controls. Users can navigate through content more efficiently by making these elements larger and easier to target.
5- Drag-and-Drop Functionality
Fitt’s Law can be applied to the design of drag-and-drop interactions. The size of draggable objects and drop targets can be adjusted to facilitate accurate and swift completion of tasks, enhancing the overall usability of such interactions.

6- Link Placement
Fitt’s Law can be used to optimize the placement of hyperlinks within web pages or applications. Links frequently clicked or deemed important can be made larger and closer to the user’s starting position to increase clickability and reduce errors.
7- Form Design
Fitt’s Law can help UX designers design forms by considering the size and positioning of input fields and buttons. Important or frequently used form elements should be larger and placed conveniently to improve user efficiency and accuracy.
Applying Fitt’s Law principles allows UX designers to create more intuitive, efficient, and comfortable user interfaces, ultimately improving the overall user experience.
Fitts’ Law Example
Fitts’ Law has left an indelible mark on the digital landscape. Its influence can be seen in the design choices of some of the world’s most renowned websites. Let’s look closer at how Fitts’ Law has shaped the user experience on these famous platforms.
1- Google
Google’s minimalist design style fully coincides with the Fitts’ Law concepts. Take a look at the size of the search bar on Google’s homepage. It is huge, highly visible, and positioned in the center, making it the major user objective. Google follows Fitts’ Law to ensure that users may easily land on the search bar, enabling speedy and accurate searches.
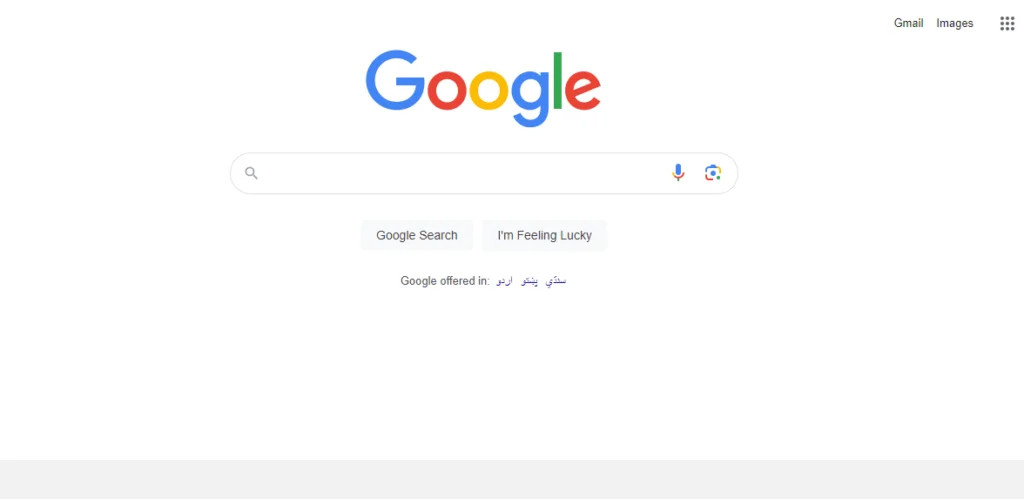
2- Amazon
Amazon, being one of the leading e-commerce platforms, has mastered the art of UI design while keeping Fitts’ Law in mind. Pay attention to the “Add to Cart” button on product pages. It’s large, contrasting in color, and strategically placed near the product features. Amazon follows Fitts’ Law to ensure that users can click the button quickly and precisely, speeding the purchasing process and improving the entire shopping experience.
3- Facebook
The law of Fitts is heavily used in designing Facebook’s interface, especially in positioning essential features. Pay attention to how the “Like” button, which is an important component of user interaction, is prominently placed beneath each post. The button is designed to be simply clickable, allowing visitors to interact with content and express their gratitude easily. Facebook’s design approach demonstrates Fitts’ Law’s power in developing intuitive and engaging user experiences.

4- Airbnb
Fitts’ Law is visible in the search functionality of Airbnb. The search bar, which is prominently displayed at the top of the homepage, is large and inviting, allowing users to focus their attention and enter their intended destination easily. Furthermore, the “Search” button, which is situated adjacent to the search bar, is created with suitable size and space, allowing users to confidently and easily perform their search.

5- Youtube
Fitts’ Law is at work in the video player interface on YouTube. The “Play” button, which is located in the center of the movie, is designed to be readily clickable and urges visitors to interact with the information without difficulty. The size and placement of this button adhere to Fitts’ Law principles, guaranteeing that viewers easily start and pause videos with minimal effort.
These examples demonstrate the extensive effect of the law of Fitts on modern website design. These well-known platforms have created straightforward, efficient, and engaging user experiences that keep users coming back for more by deliberately implementing Fitts’ Law principles.
Summary
Fitts’ Law is a crucial pillar of UX design, enhancing how we interact with interfaces and shaping unforgettable experiences. By embracing its principles, designers create visually stunning, intuitive, and efficient UIs that capture users’ hearts and minds. So, let Fitts’ Law be your guiding star, leading you towards UX design excellence, where every interaction tells a story and every click brings joy.
FAQs
How did the law of Fitts originate?
The Law of Fitts, named after psychologist Paul Fitts, was initially established in the field of human movement research in 1954. Paul Fitts carried out a series of tests to learn how people make targeting movements like pointing at targets. His study sought to determine the key parameters that influence the time required to accomplish these actions correctly.
Difference between Fitts law and hicks law.
Fitts’ Law predicts the time required to move to a target based on its size and distance, while Hick’s Law predicts the time it takes to decide based on the number of choices available.
