User experience design is all about creating enjoyable and intuitive digital interactions. One approach that’s been making waves in recent years is gamification. By integrating game-like elements into UX design, businesses can capture users’ attention, motivate them, and keep them coming back for more.
In this blog, we’ll explore what gamification is, why it works, and how you can use it to create engaging, retention-focused user experiences.

What is Gamification in UX?
Gamification in UX involves adding game-like features to non-gaming contexts, such as apps, websites, or digital platforms. These features motivate users to engage with the product in a fun and rewarding way.
Some common gamification elements include:
- Points: Rewarding users for completing specific actions.
- Badges: Visual tokens for achieving milestones or goals.
- Leaderboards: Ranking systems that foster competition.
- Progress Bars: Visual indicators that show how close users are to achieving a goal.
- Challenges: Tasks or objectives that encourage users to take action.
For instance, Duolingo uses points, streaks, and rewards to keep users motivated while learning languages. Fitbit encourages users to stay active by rewarding badges for hitting fitness goals. These features not only make the experience enjoyable but also tap into psychological triggers that drive engagement.
The Psychology Behind Gamification
To understand why gamification works, it’s essential to delve into the psychology behind it. Gamification taps into fundamental human motivations and behaviors.
Intrinsic vs. Extrinsic Motivation
- Intrinsic Motivation: This comes from within. People are intrinsically motivated when they engage in an activity because they find it enjoyable or fulfilling.
- Extrinsic Motivation: This stems from external rewards, such as points, badges, or prizes.
Gamification appeals to both types of motivation. For example, a progress bar provides extrinsic motivation by showing a tangible reward (completion). Simultaneously, it leverages intrinsic motivation by making users feel accomplished.
The Role of Dopamine
Gamified interactions trigger the brain’s reward system, releasing dopamine. This “feel-good” chemical reinforces behavior, encouraging users to repeat the activity. For example, completing a task and earning a badge provides immediate gratification, making users want to achieve the next milestone.
Behavioral Design Principles
Gamification aligns with behavioral psychology principles like:
- Habit Loops: Repetition of a cue, routine, and reward creates habits.
- Positive Reinforcement: Rewards encourage users to continue desired behaviors.
- Social Proof: Leaderboards and peer comparisons motivate users to perform better.
Also read: Color Psychology in UX: How They Influence User Behavior
Types of Gamification
Gamification can be categorized into different types based on the goals and mechanics used. Here are the main types:
1. Progress-Based Gamification

This type focuses on tracking user advancement through clear visual indicators. By showing how far users have come and what lies ahead, it keeps them motivated to achieve more.
Examples:
- Progress bars in applications like LinkedIn for completing profile information.
- Levels or stages in e-learning platforms like Khan Academy.
Key Benefits:
Provides a sense of accomplishment and direction.
Encourages users to stay on track with tasks and goals.
2. Competitive Gamification
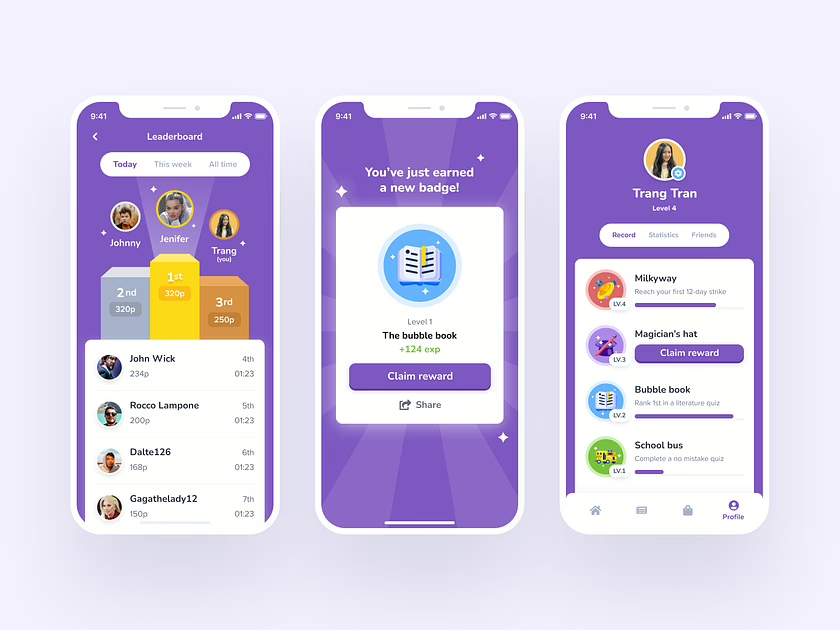
Competition is a powerful motivator, appealing to users who thrive on outperforming others or achieving recognition.
Examples:
- Leaderboards in fitness apps like Fitbit or Strava, ranking users based on activity levels.
- Multiplayer challenges in gaming-inspired apps.
Key Benefits:
- Fosters engagement through rivalry and performance benchmarks.
- Drives users to return and improve their rankings.
3. Reward-Based Gamification
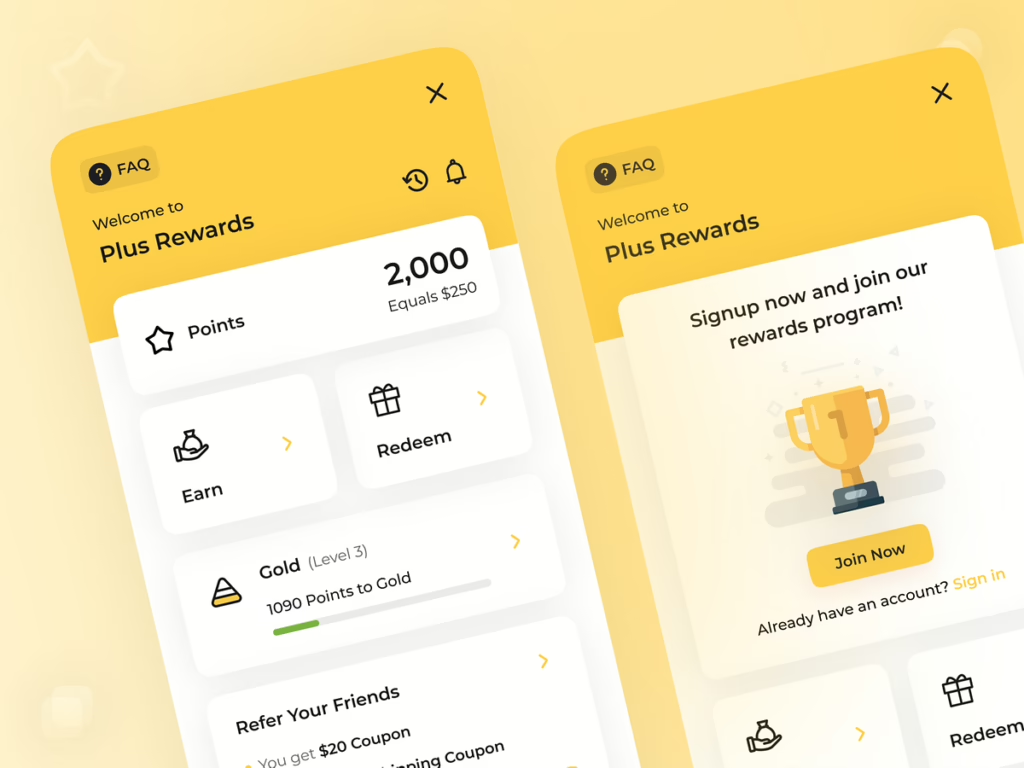
Reward systems directly incentivize users for completing actions or reaching milestones. This taps into extrinsic motivation by offering tangible or symbolic rewards.
Examples:
- Points in Starbucks Rewards that accumulate for free drinks or merchandise.
- Badges in Duolingo, celebrating streaks or learning achievements.
Key Benefits:
- Encourages loyalty and consistent participation.
- Makes achieving goals feel gratifying and worthwhile.
4. Social Gamification
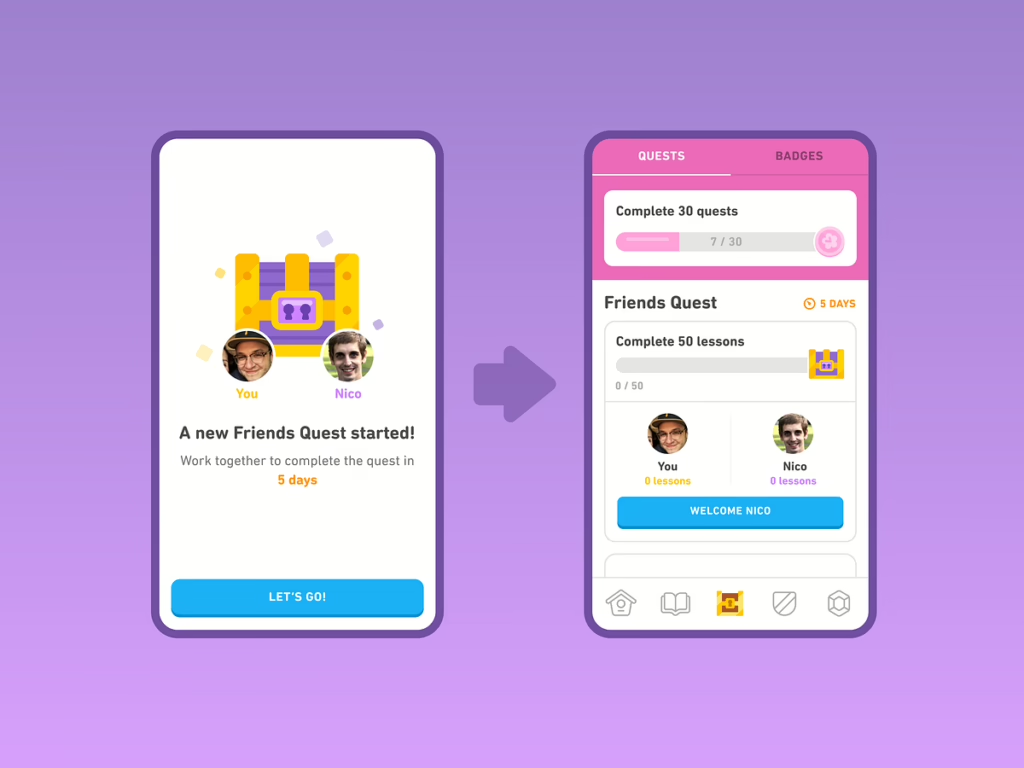
By incorporating elements that promote collaboration and community, this type enhances user interaction and engagement.
Examples:
- Team-based challenges in apps like Habitica, where users complete tasks collectively.
- Social sharing incentives, such as Instagram’s badge system for top contributors.
Key Benefits:
- Builds a sense of belonging and camaraderie.
- Encourages users to invite friends, amplifying app visibility.
5. Exploratory Gamification
For users who enjoy curiosity-driven exploration, this type introduces hidden surprises, challenges, or opportunities to discover new content.
Examples:
- Easter eggs in Google products like hidden games in Chrome.
- Quests in productivity apps that unlock new tools or features.
Key Benefits:
- Stimulates curiosity and keeps the experience dynamic.
- Encourages deeper interaction with the platform.
Integrating Gamification Types
The most successful gamification strategies often combine multiple types.
For instance, an app might use progress-based gamification to motivate goal completion, reward-based systems to reinforce achievements, and social elements to enhance collaboration. Tailoring the approach to your audience ensures maximum effectiveness and user satisfaction.
Also read: Sustainable UX/UI Design | Why It Matters and How to Start
Benefits of Gamification in UX
1- Increased Engagement
Gamification transforms ordinary tasks into interactive and enjoyable experiences. Features like streaks, rewards, and progress tracking encourage users to spend more time on the platform. For example, Duolingo’s daily streak motivates users to return regularly.
2- Improved Retention
Retaining users is a major challenge for digital platforms. Gamified experiences foster loyalty by keeping users entertained and invested. Rewards, challenges, and social interactions make them feel connected to the platform.
3- Enhanced Learning and Productivity
Apps like Khan Academy and Quizlet gamify education, making learning fun and effective. Similarly, productivity tools like Habitica turn task management into a game, helping users stay focused and organized.
4- Social Interaction
Gamification fosters community and competition. Features like leaderboards, challenges, and team-based goals encourage social interaction. This adds a layer of fun and motivates users to perform better.
How to Effectively Use Gamification in UX Design
To make gamification work, you need a thoughtful approach. Here are some best practices:
1- Understand Your Audience
Users respond differently to gamification. Research your target audience to understand their preferences, motivations, and behaviors. Then tailor the gamification elements to align with their needs.
2- Focus on Simplicity
Gamified features should be easy to use. Overloading users with too many elements can lead to confusion and frustration. Start small and add complexity gradually.
3- Create Clear Goals and Rewards
Users need to know what they’re working towards. Clearly define goals and ensure the rewards are meaningful. For example, completing a series of tasks could unlock a premium feature or exclusive content.
4- Balance Challenge and Skill
If a task is too easy, users will get bored. If it’s too hard, they’ll get frustrated. Find the right balance by gradually increasing the level of challenge as users improve.
5- Avoid Overuse
While gamification can be powerful, overusing it can feel forced and detract from the overall experience. Use it strategically to enhance key parts of your UX.

Challenges and Limitations of Gamification
1- User Fatigue
Gamification elements like streaks and rewards can lose their appeal if overused. Users may grow tired or feel pressured, leading to disengagement.
2- Ethical Considerations
Gamification can be manipulative if not implemented ethically. For example, creating addictive loops may harm users’ well-being. Designers should prioritize user benefit over profit.
3- Cost and Development Time
Creating effective gamification features requires time, resources, and expertise. Small businesses with limited budgets may find this challenging.
4- One-Size-Fits-All Doesn’t Work
Different users have different preferences. A gamification strategy that works for one group may not work with another. Personalization is key to addressing this limitation.
Examples of Gamification in UX
Duolingo
Duolingo gamifies language learning with streaks, progress bars, and leaderboards. These features make the process enjoyable and motivate users to stay consistent.
Fitbit
Fitbit rewards users with badges for hitting fitness milestones. Social challenges allow users to compete with friends, adding an element of fun to staying active.
Starbucks Rewards
Starbucks uses gamification to drive customer loyalty. With every purchase, users collect stars that can be redeemed for free items. Seasonal challenges and personalized rewards keep the experience fresh and engaging.
Future Trends in Gamification and UX
1- AI and Personalization
Artificial intelligence can create personalized gamification experiences based on user behavior. For example, an AI-powered app could recommend challenges tailored to a user’s interests.
2- AR/VR Integration
Augmented and virtual reality are opening up new possibilities for gamification. Immersive experiences can make users feel like they’re part of the game.
3- Blockchain-Based Rewards
Blockchain technology enables transparent and secure reward systems. Digital tokens or NFTs could be used as incentives in gamified experiences.
4- Sustainability and Purpose-Driven Gamification
Gamification can be used to promote social and environmental good. For example, apps like EcoAction reward users for reducing their carbon footprint.
Steps to Get Started with Gamification in UX
- Research Your Audience: Understand what motivates them and what challenges they face.
- Identify Opportunities: Pinpoint areas in your product where gamification could add value.
- Design Gamified Features: Create elements that align with user goals and preferences.
- Test and Iterate: Collect feedback and refine your approach to ensure the gamified experience is effective.
Conclusion
Gamification in UX is a powerful tool for engaging and retaining users. By incorporating elements like points, badges, and progress bars, you can create memorable experiences that keep users coming back. However, it’s important to use gamification thoughtfully and ethically to ensure it truly benefits your audience.
If you’re ready to take your UX to the next level, Hapy Design is here to help. We specialize in crafting user-centered designs that engage, motivate and delight.
Let’s work together together to create something unique. Contact us now.